Commuter Rail Safety and Resiliency Program

Positive Train Control (PTC) Automatic Train Control (ATC)
The Rail Safety Improvement Act of 2008 requires every railroad across the country to have Positive Train Control (PTC).
We completed Phase I of the Commuter Rail Safety and Resiliency Program in August 2020. The MBTA PTC system is now active on all Commuter Rail lines. Phase II was completed in 2024, with ATC implemented on all Commuter Rail lines. Phase III, Fiber Optic Resiliency, is now underway with a projected completion of 2025.
Building a Better T
As part of our $9.6 billion, 5-year capital investment plan, we're renovating stations, modernizing fare collection systems, upgrading services for our buses, subways, and ferries, and improving the accessibility of the entire system.
In Progress
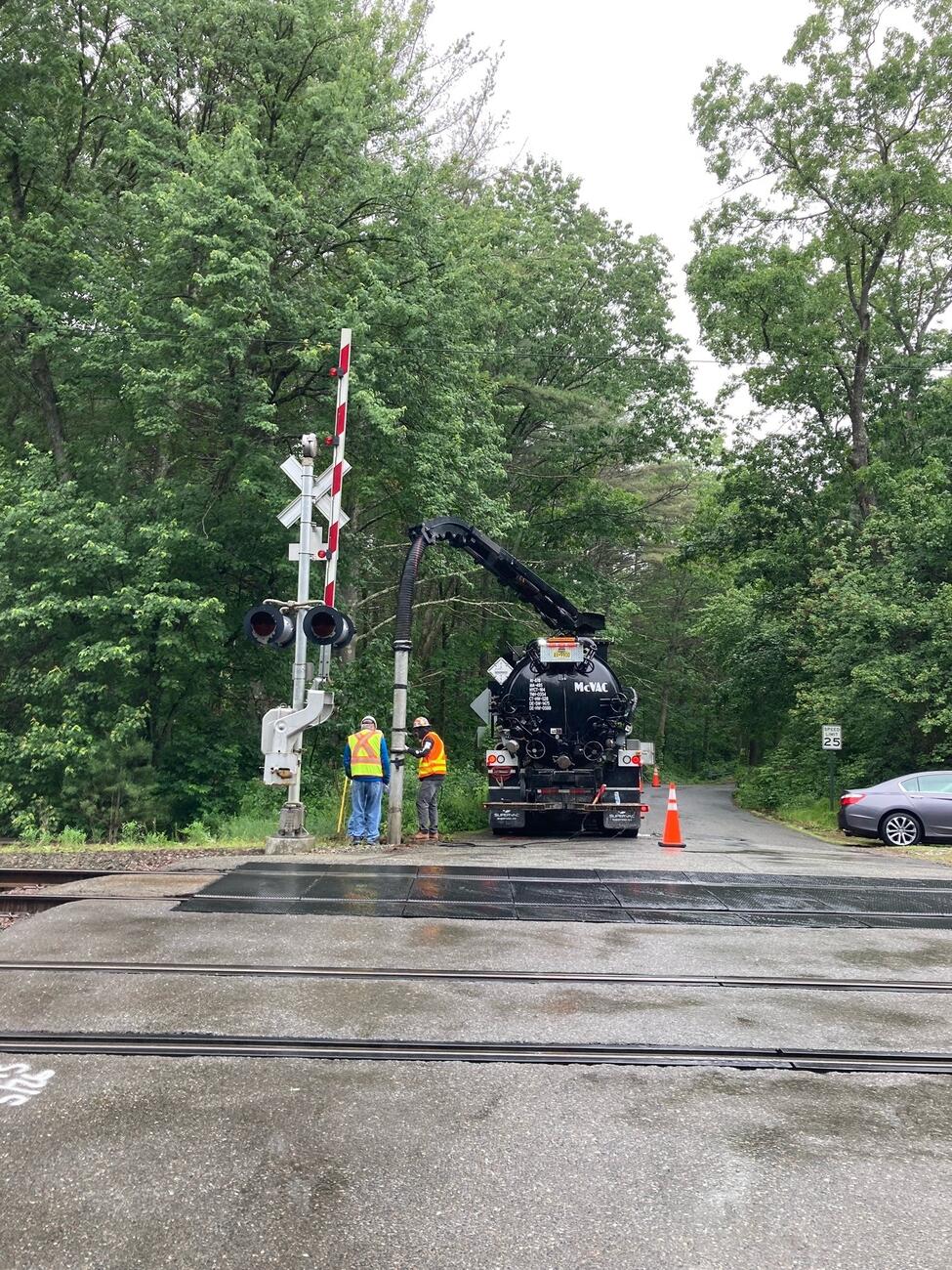
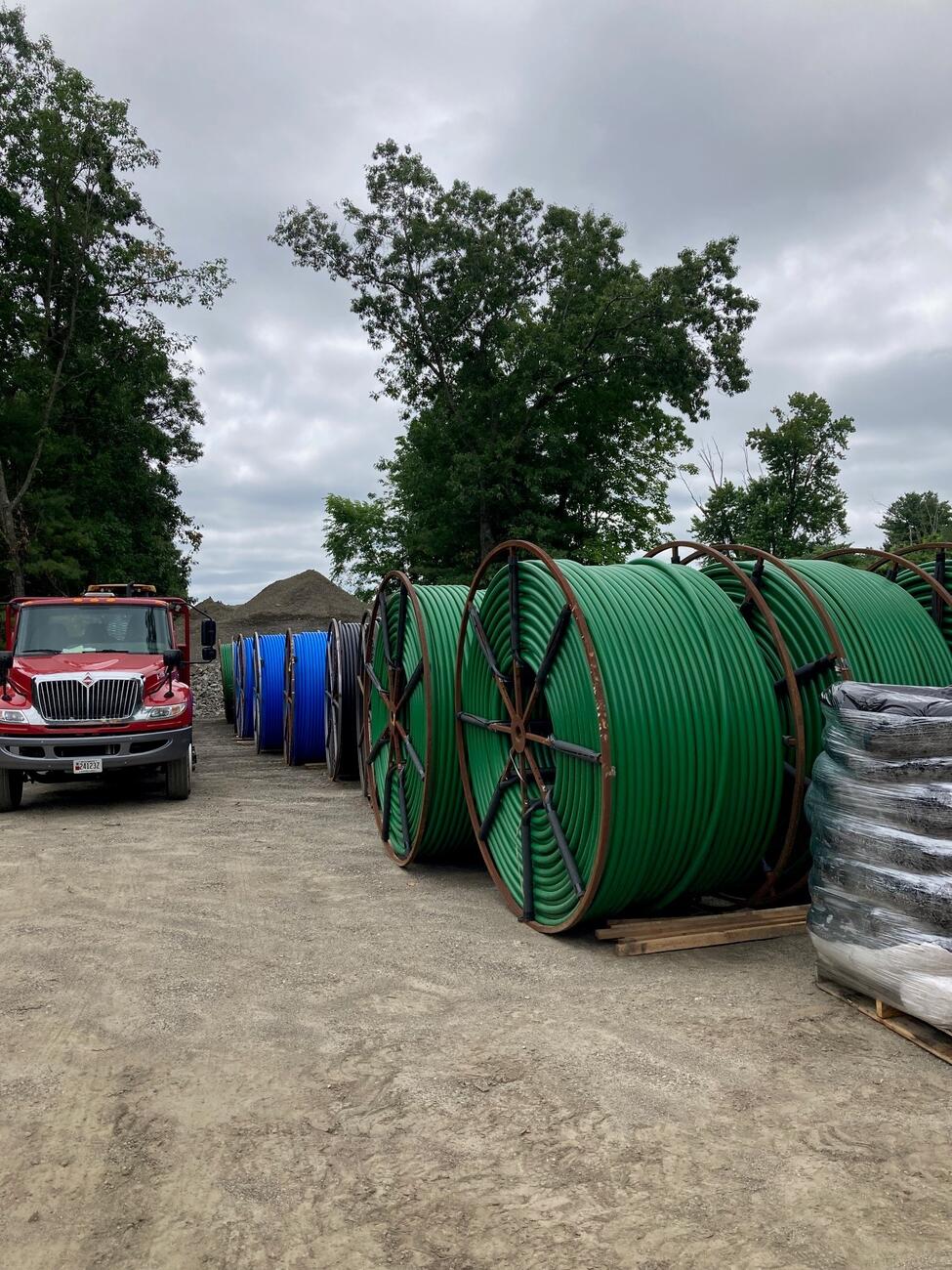
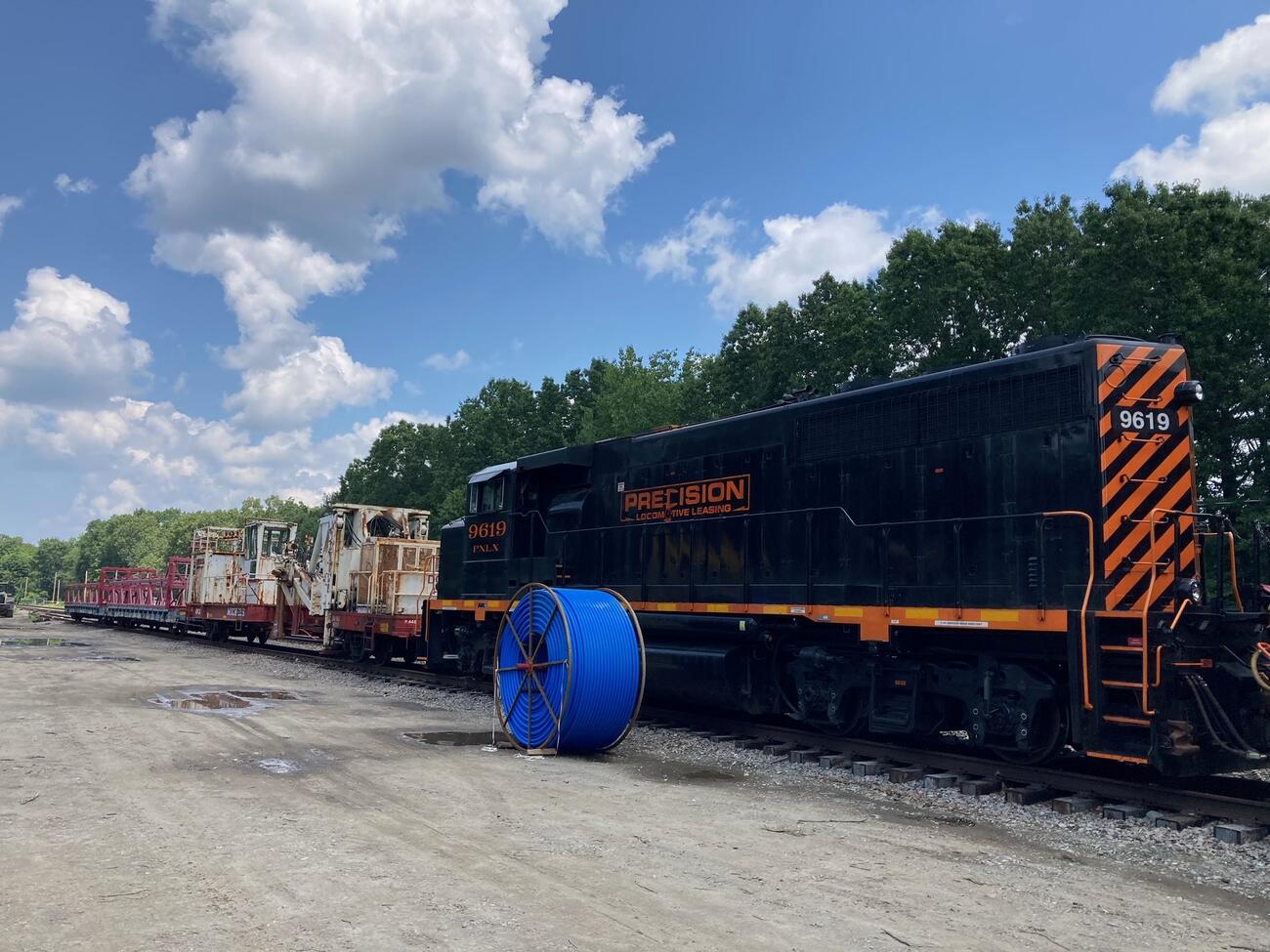
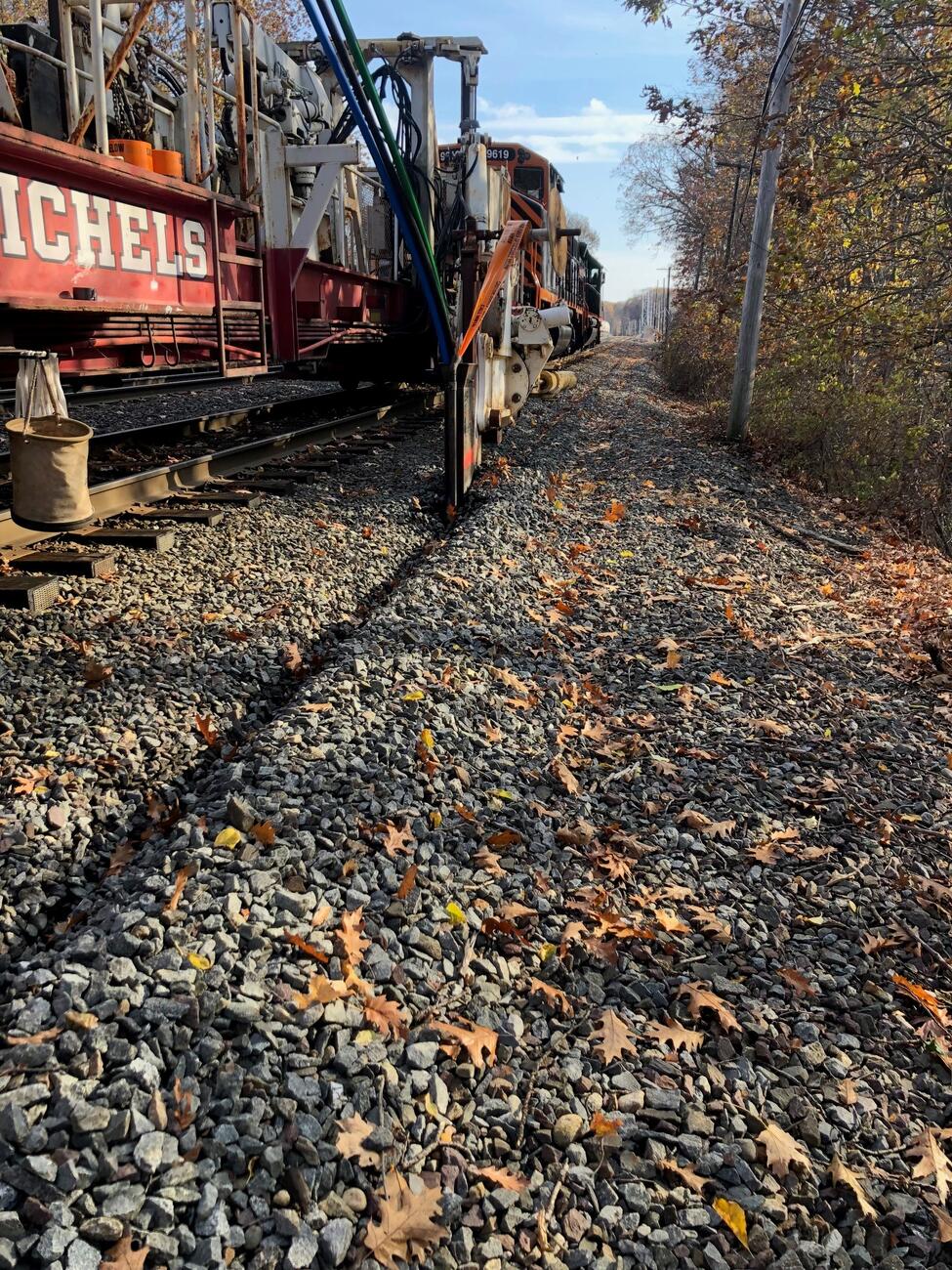
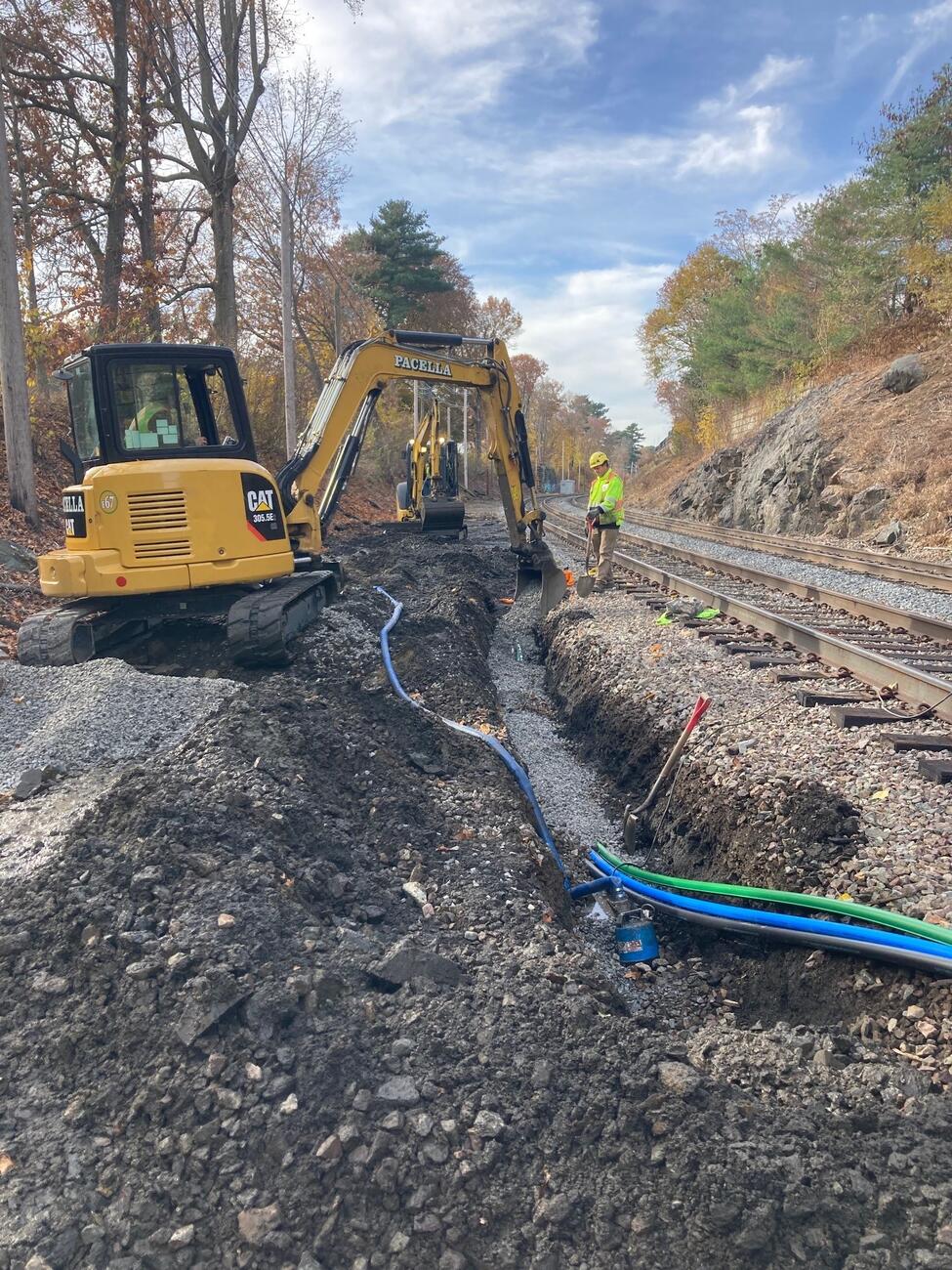
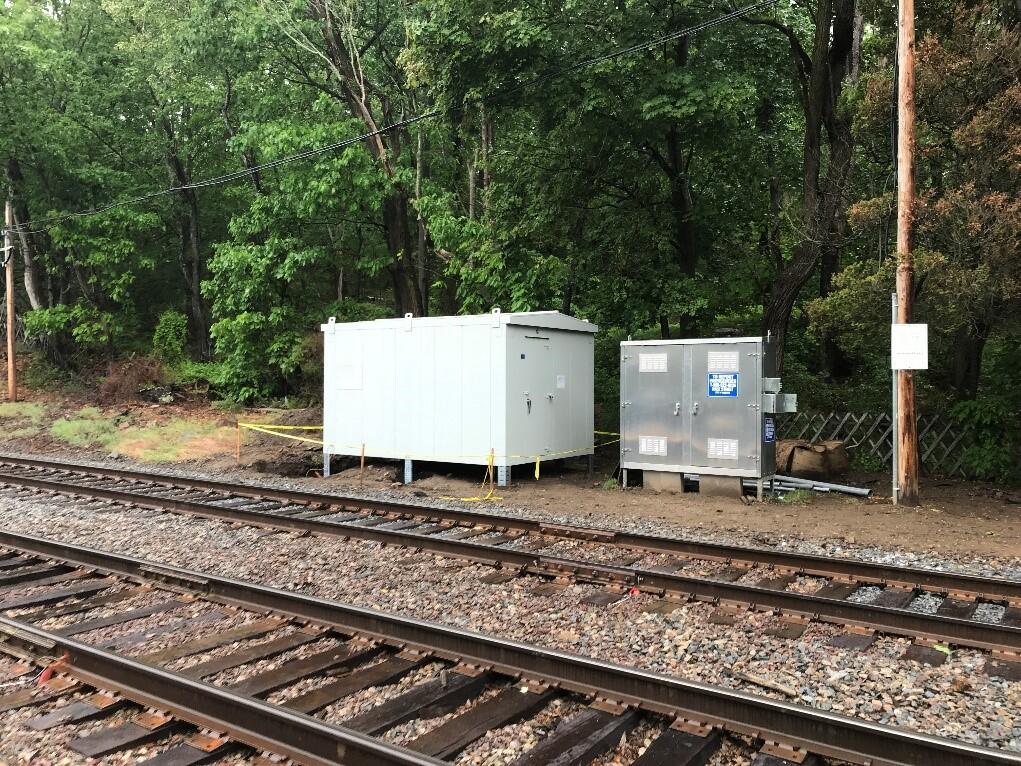
Phase III: Fiber Optic Resiliency (FOR) (2022 – 2025)
This project will create a buried fiber optic cable network for signals, communications, and PTC systems between or alongside Commuter Rail tracks where aerial systems exist today.
The FOR project is responsible for planning, designing, installing, and testing a buried fiber optic cable network that will provide resilient infrastructure to support MBTA PTC vital systems operating on weather-exposed aerial infrastructure.
The current scope includes the design and installation of a buried fiber optic cable network between or alongside Commuter Rail tracks along the Fitchburg and Lowell lines.
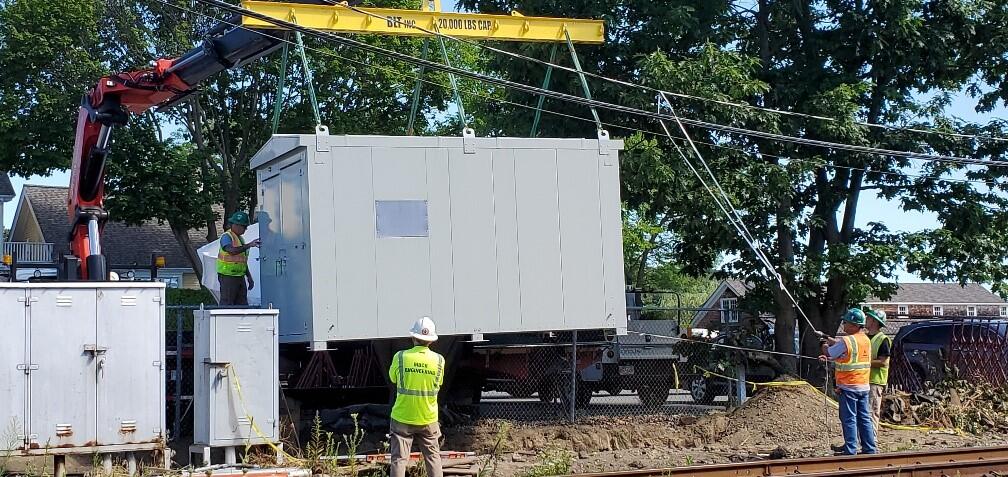
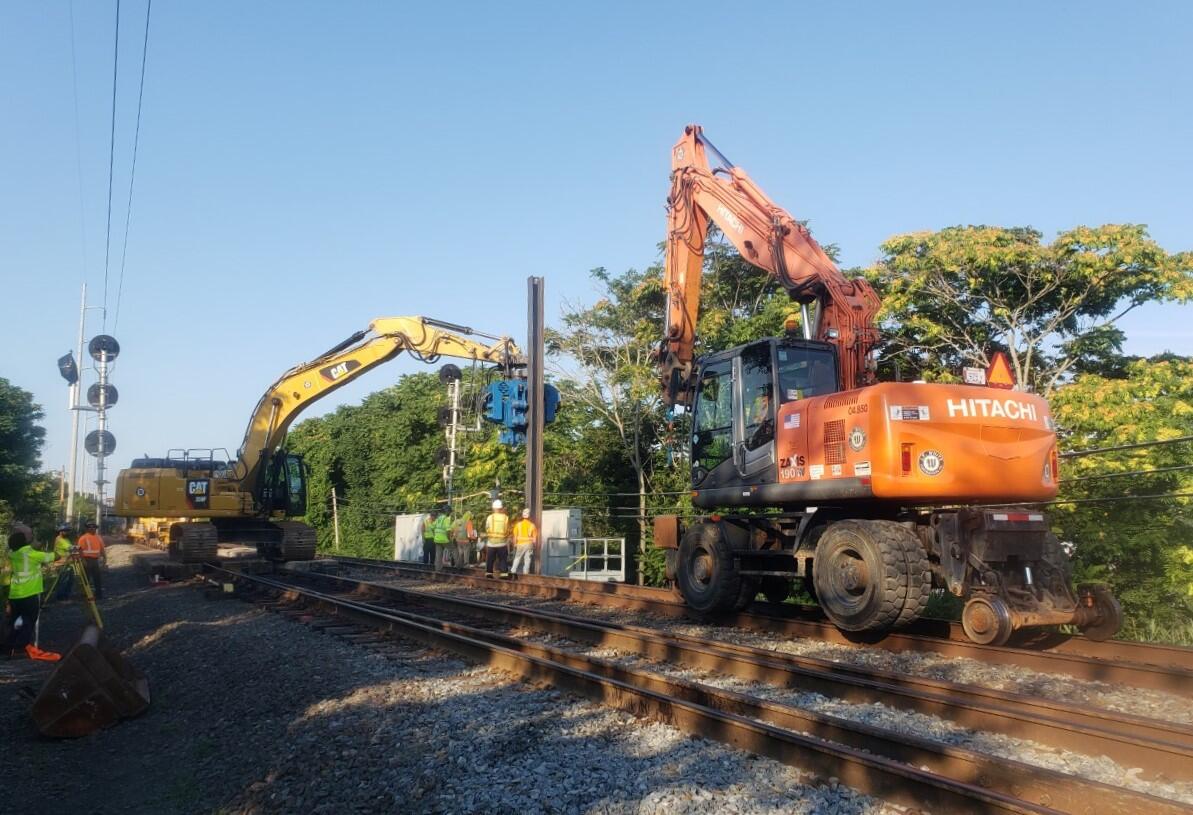
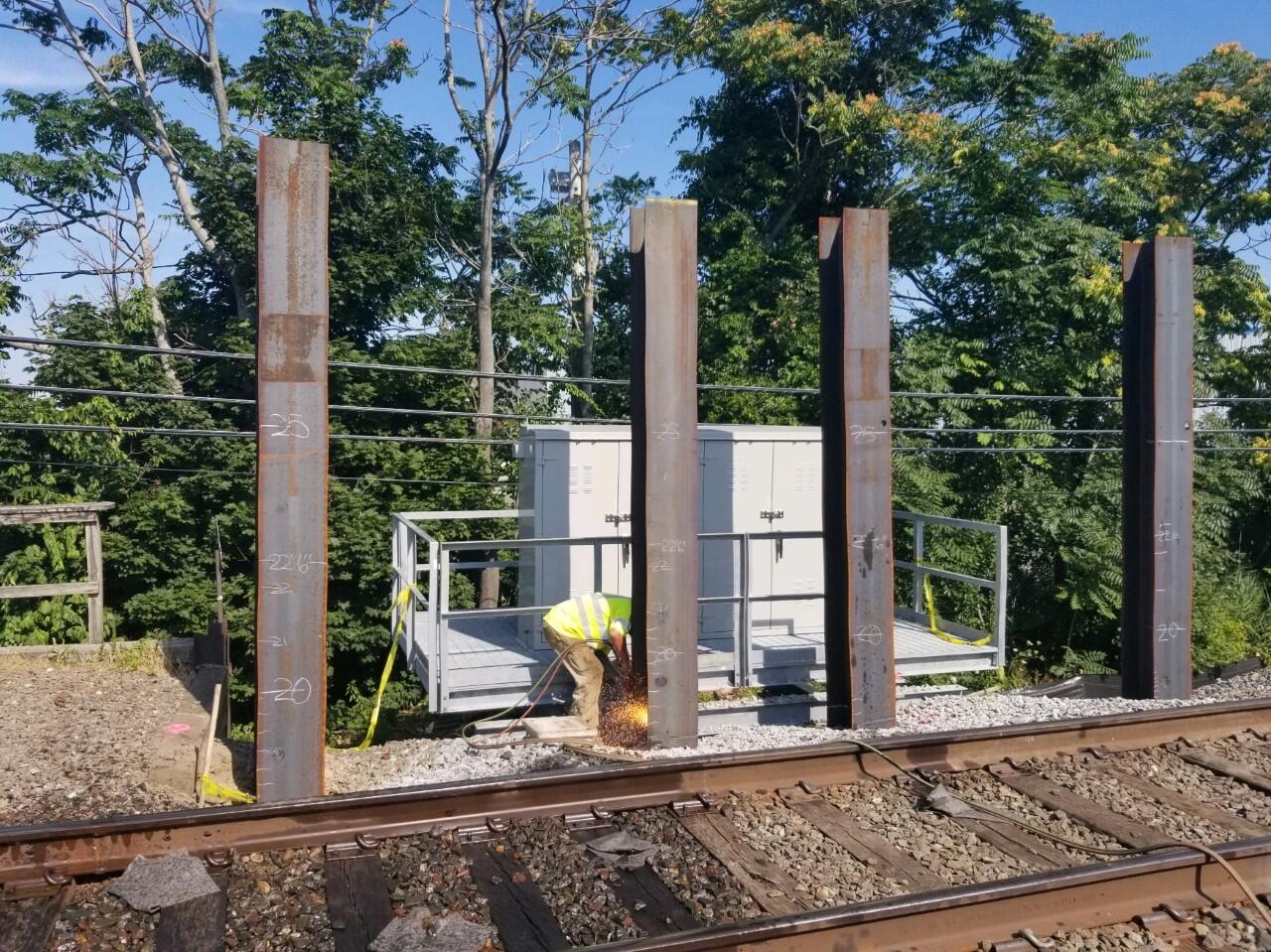
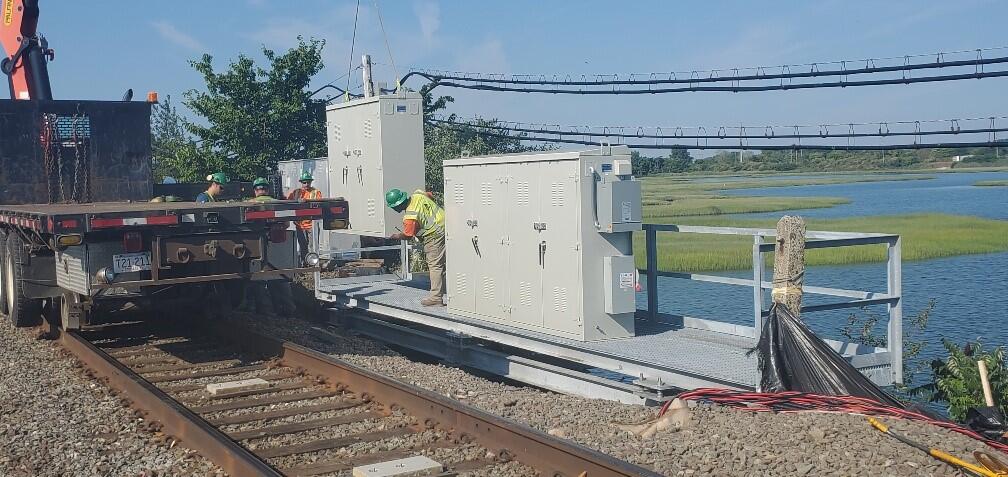
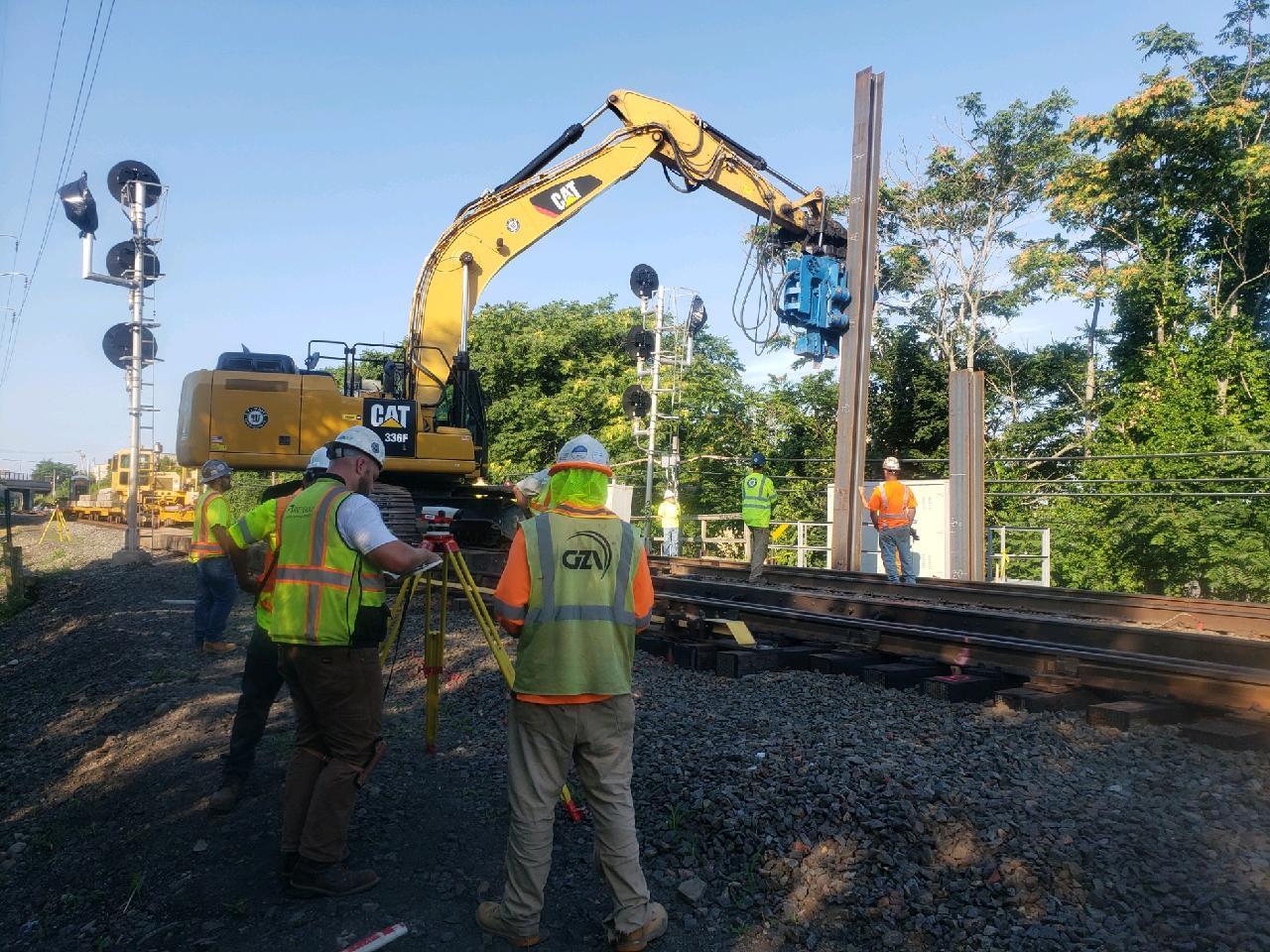
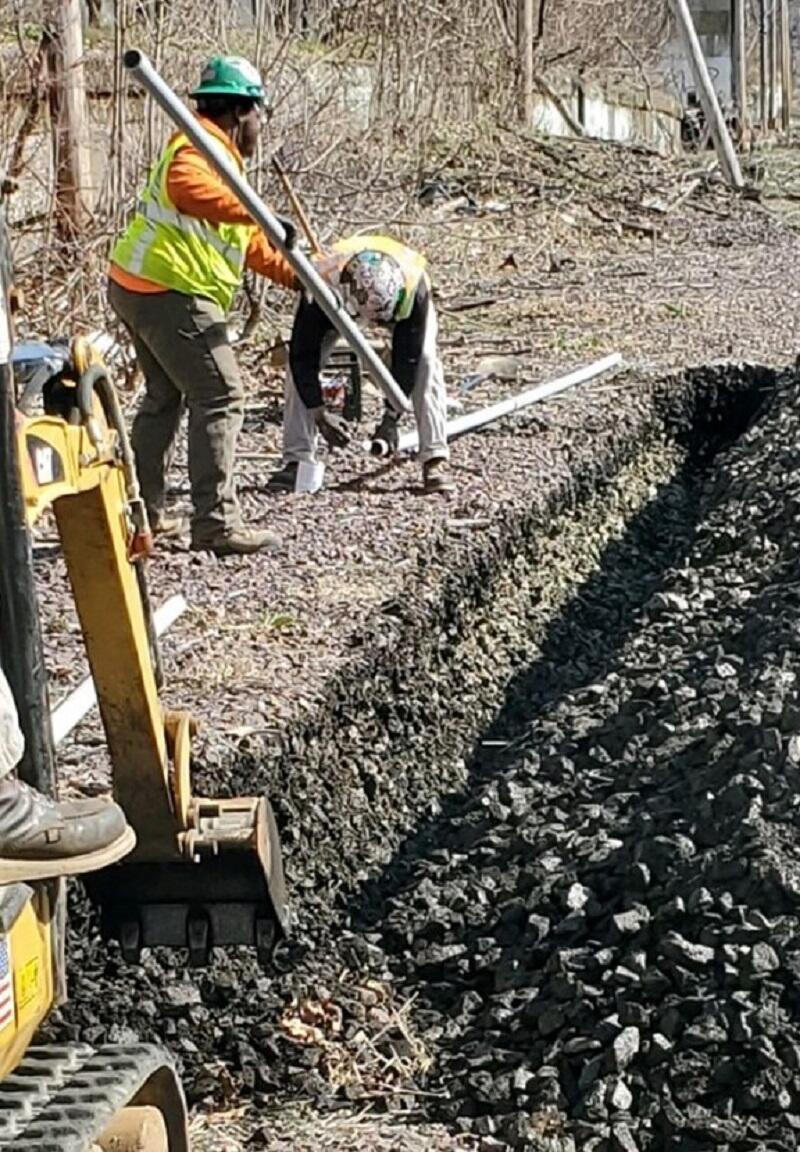
Fiber Optic Resiliency Project Progress
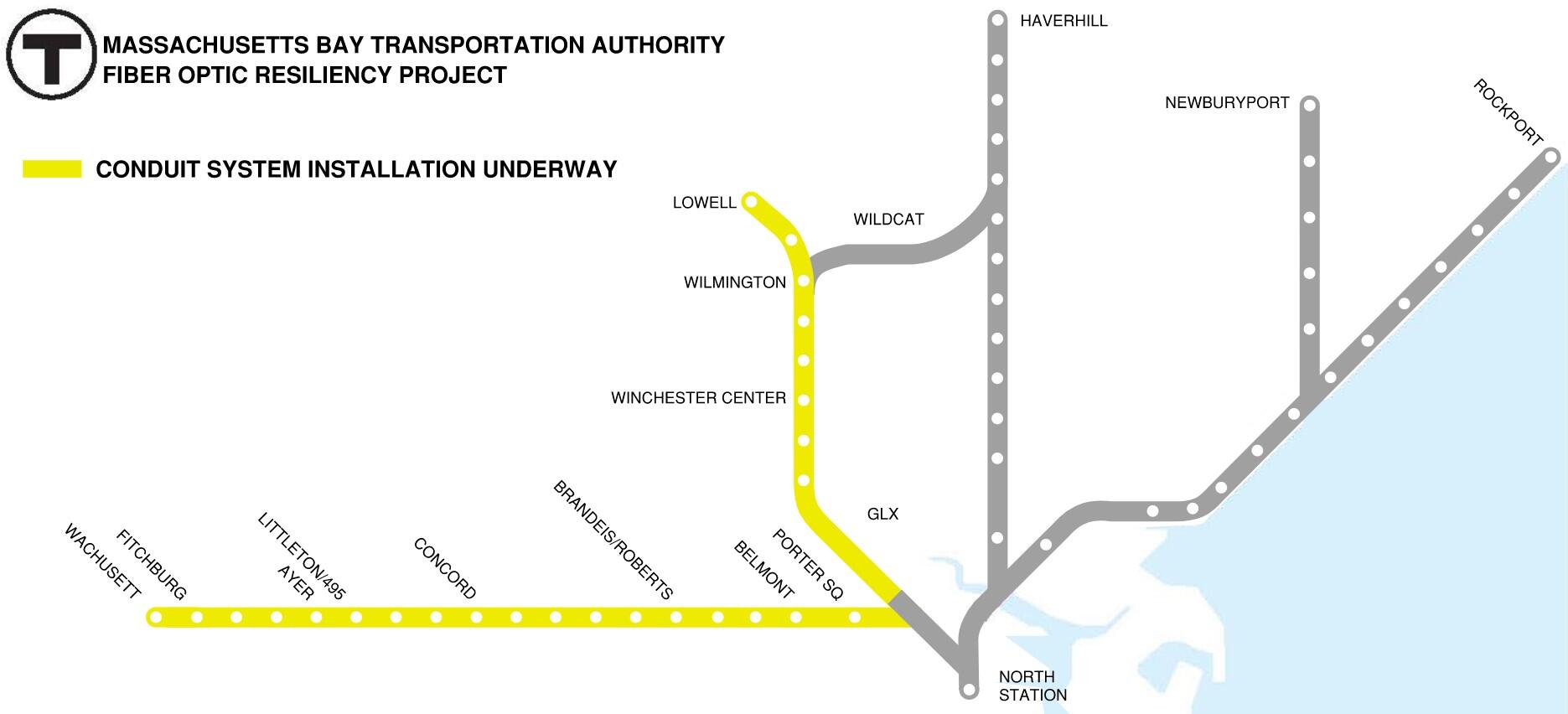
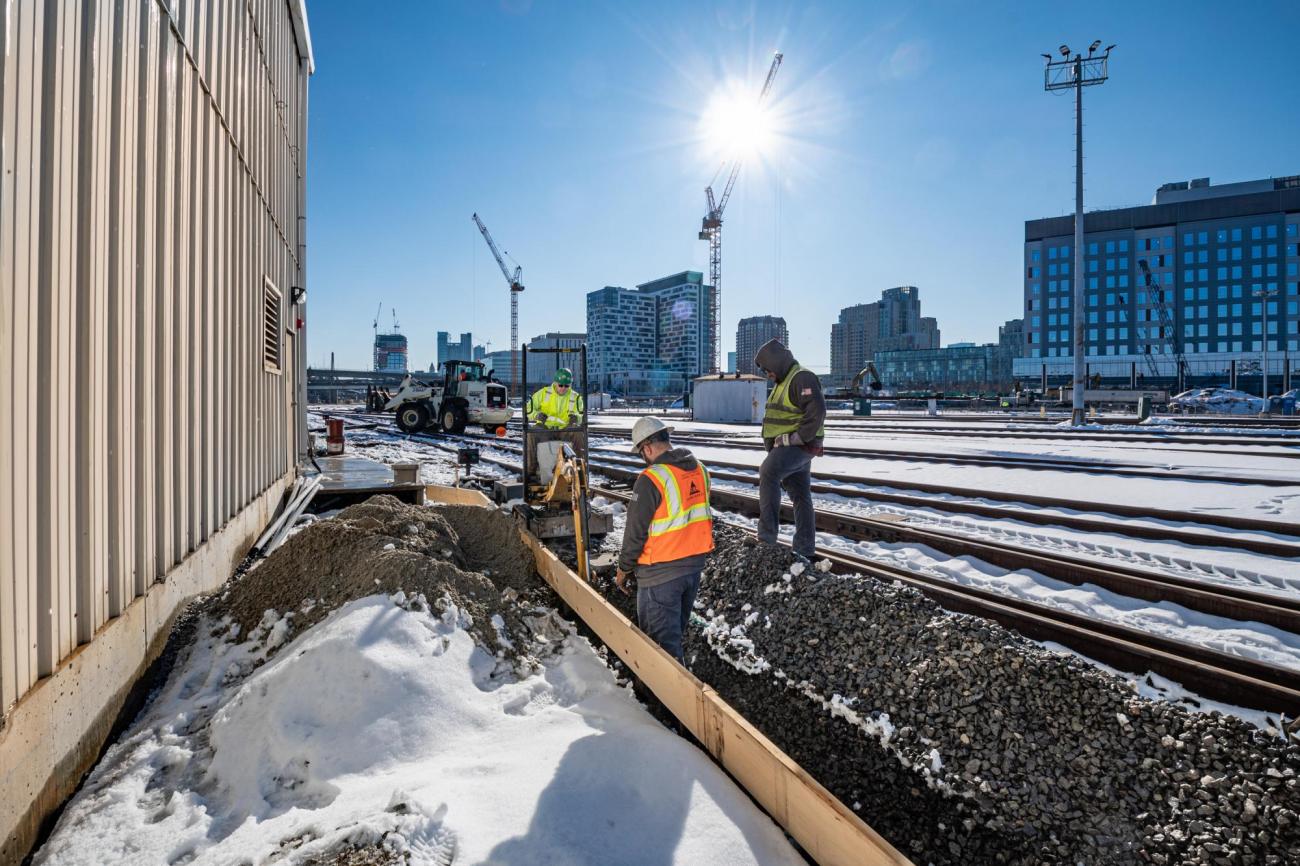
FOR Construction began in August 2023.
Overnight work on the Fitchburg line will begin on Sunday, May 19, 2024, through Saturday, June 22, 2024.
- Crews will be working from 9 PM - 5 AM, Sunday - Thursday.
- Crews will mobilize at Brandeis Station in Waltham and move along the railroad Right-of-Way between Concord Avenue in Belmont and Route 28/McGrath Highway in Somerville.
Residents can expect lights and moderate noise levels from the construction equipment.
FOR construction began in March 2024. Residents can expect lights and moderate noise levels from the construction equipment.
Phase III Photo Gallery
Complete
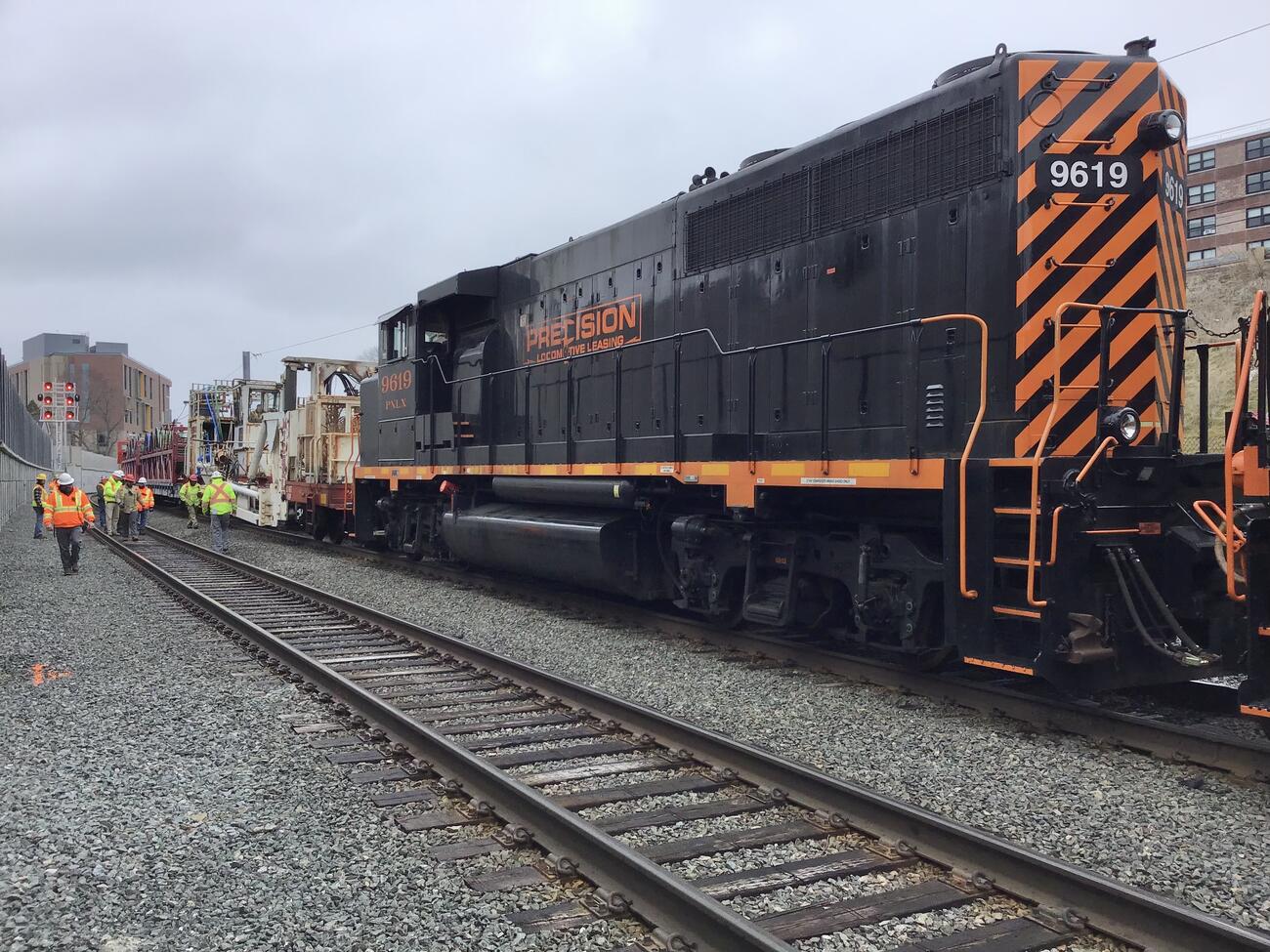
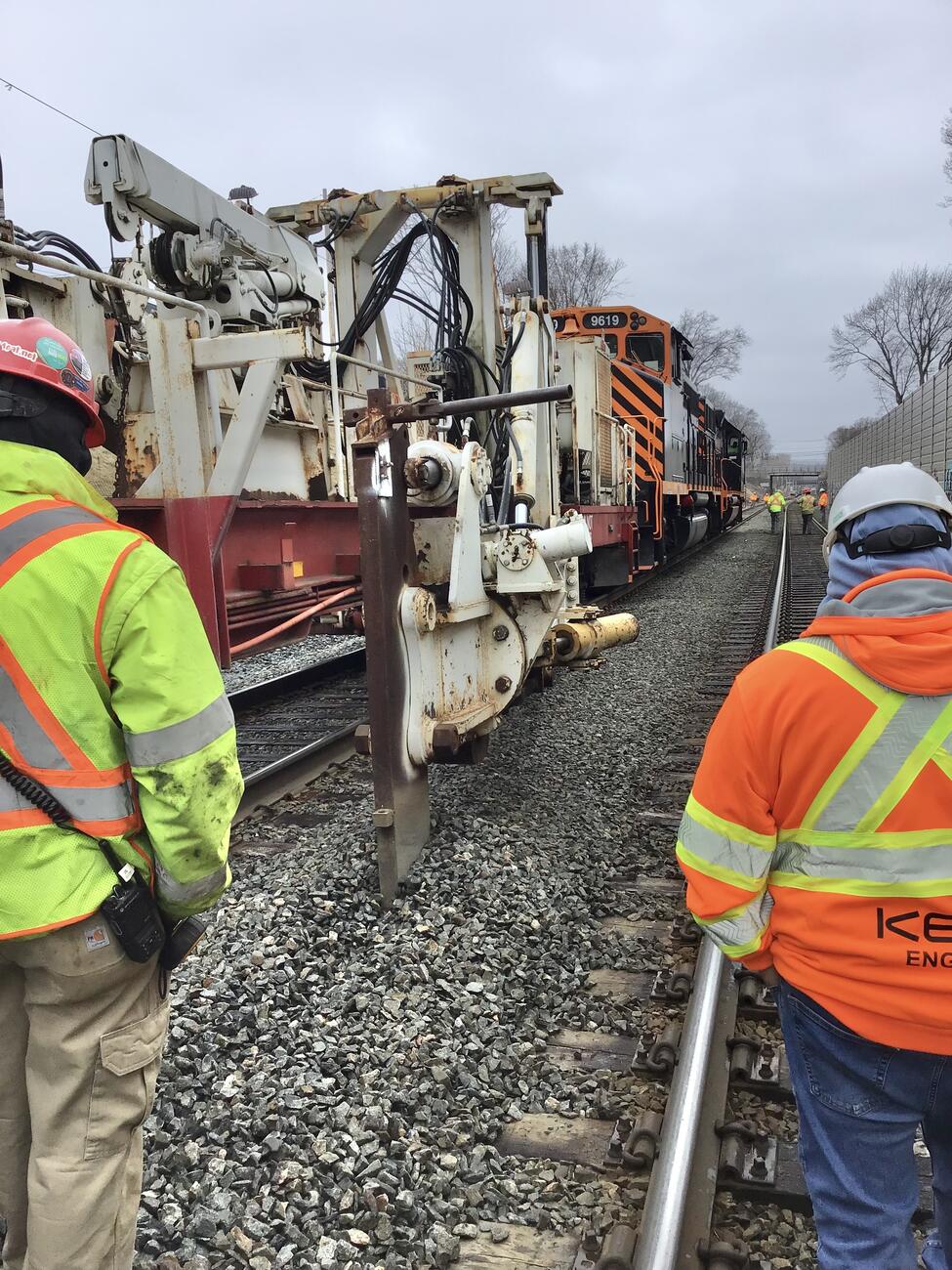
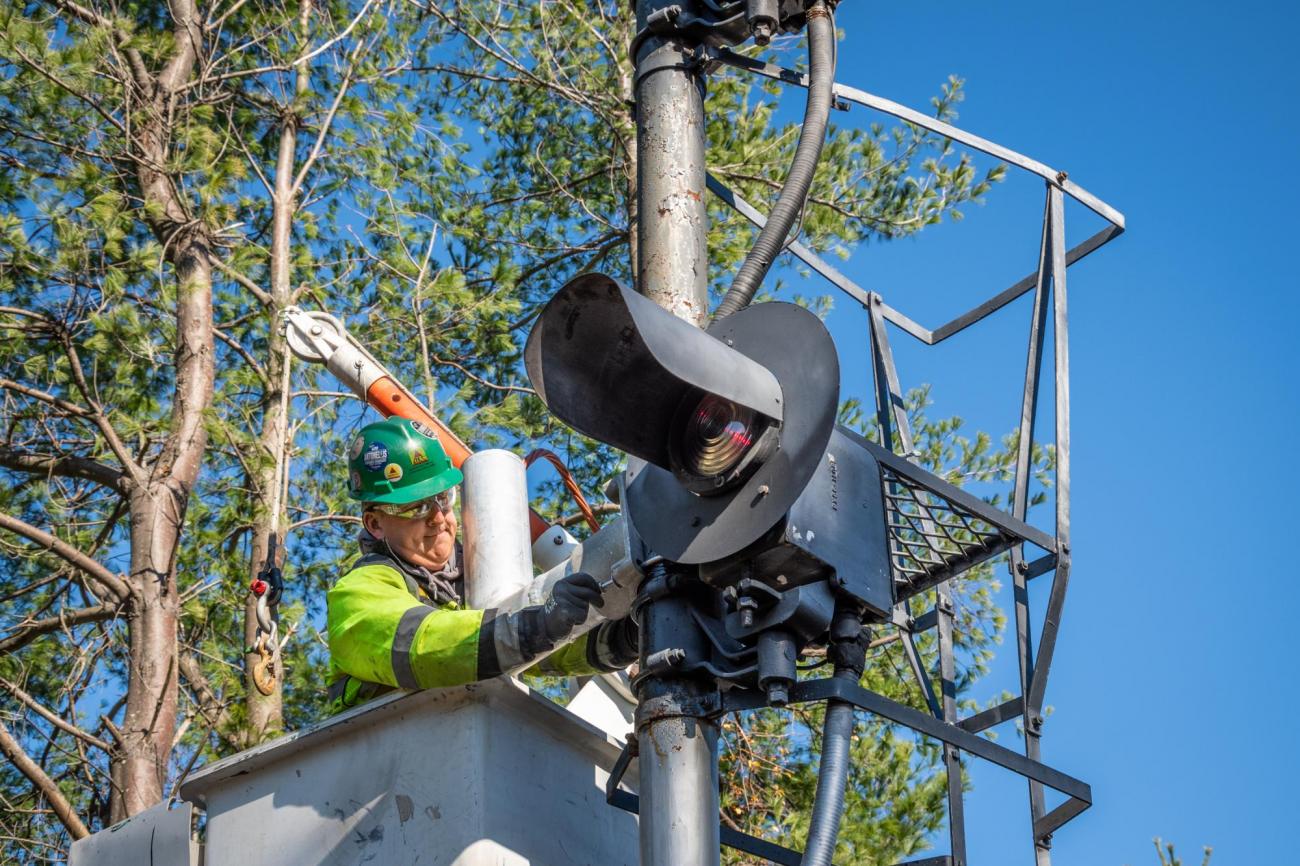
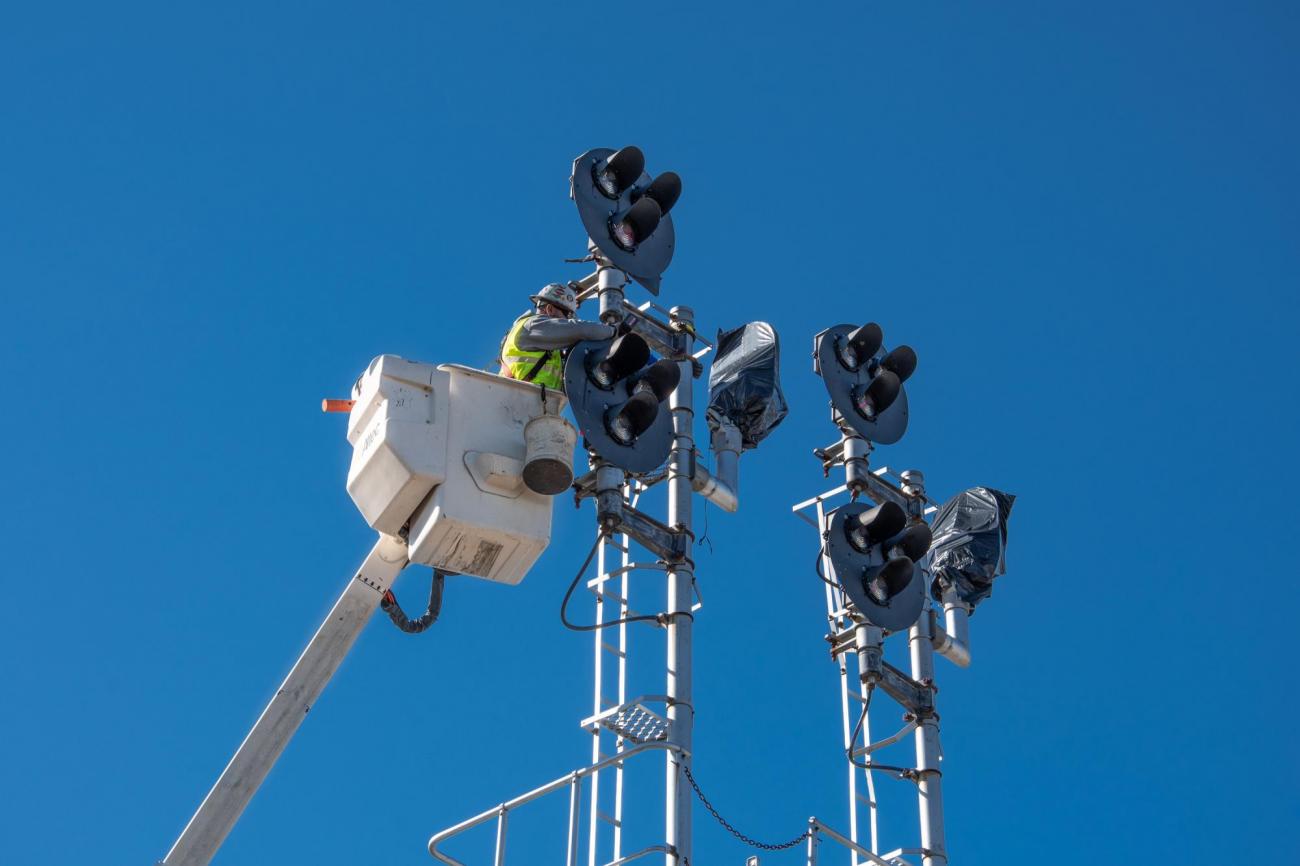
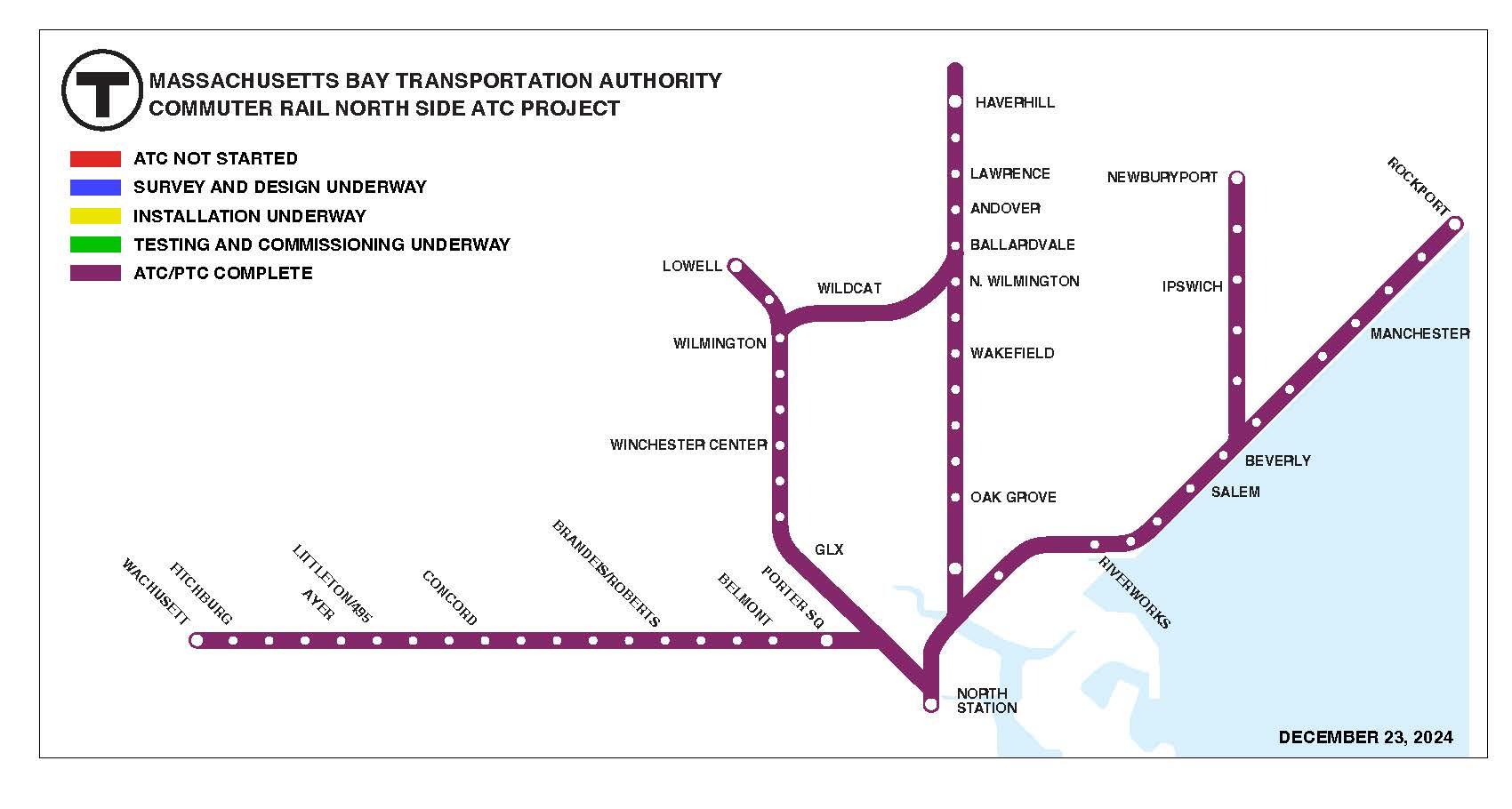
Phase II: Automatic Train Control (ATC) (2020 – 2024)
Phase II included implementation of Commuter Rail Automatic Train Control (ATC) as part of the MBTA PTC System.
- Phase II for Commuter Rail Lines out of South Station: Successfully completed on time in 2020
- Phase II for Commuter Rail Lines out of North Station: Successfully completed on time in 2024.
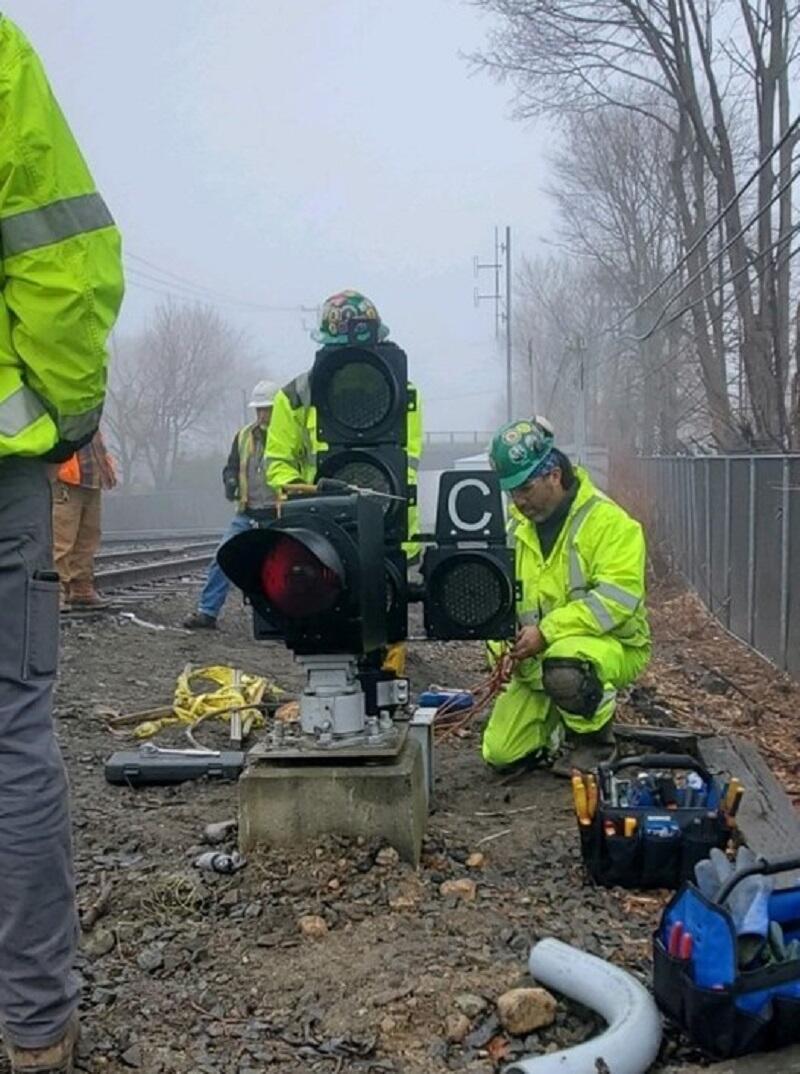
Automatic Train Control (ATC) sends signal indications to the train cab in addition to using physical signal lights alongside the tracks. These signals are part of the MBTA Positive Train Control (PTC) System that alert the engineer of potentially unsafe conditions.
If the crew does not respond to an alert, the system will automatically slow or stop the train.
ATC is an upgrade to the existing signal system and is required by the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) as part of the PTC System implementation.
The MBTA Positive Train Control (PTC) System requires Automatic Train Control (ATC) to achieve the greatest level of safety and is required by federal regulation.
ATC is now in operation as part of the signal system on all lines.
Automatic Train Control Implementation
ATC is complete and active on the following lines:
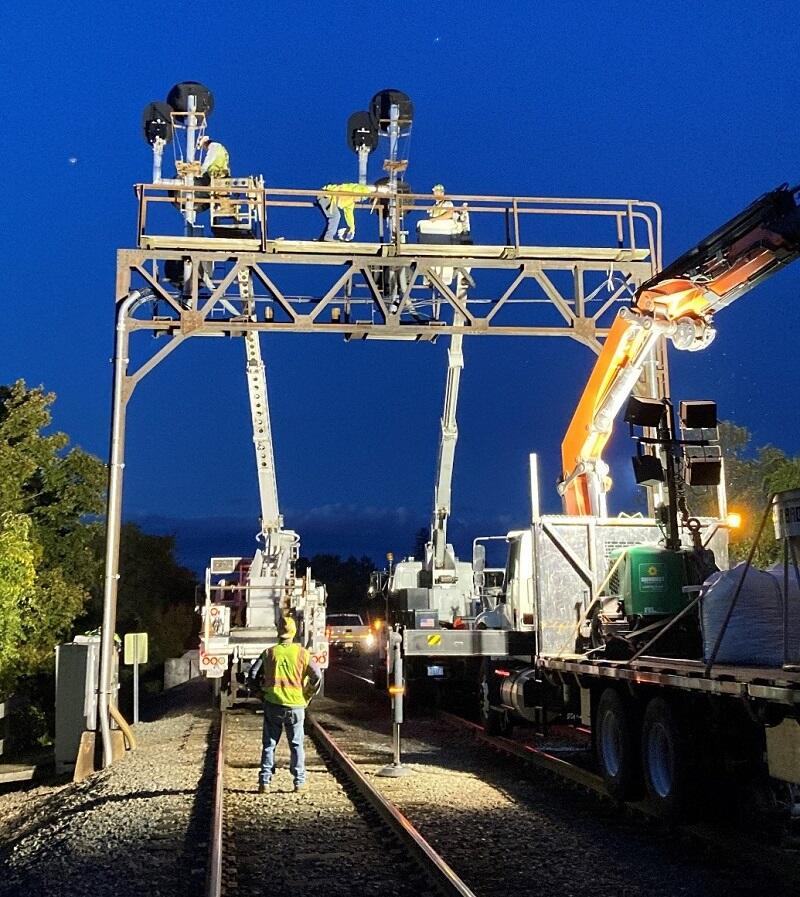
Phase II Photo Gallery
Phase I: Positive Train Control (PTC) (2017 – 2020)
The MBTA PTC system implements the Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System (ACSES), a proven system used by all systems on the Amtrak Northeast Corridor which runs through eight states from Washington DC up to Boston.
Positive Train Control (PTC) is a train monitoring system that alerts the engineer when it detects the possibility of either a train-to-train collision or a train that's moving too fast along the line or through a work zone.
The MBTA's PTC system is also designed to prevent unexpected movement of trains through "open switches." The safety technology monitors a train’s location, direction, and speed in real time.
If the crew does not respond to an alert, PTC will take over and automatically stop the train.
The PTC safety system works through:
- Signals and transponders along the rail corridor that transmit data to the train
- Onboard controls that can regulate a train’s speed
- Communications throughout the Commuter Rail network
PTC on the MBTA Commuter Rail System
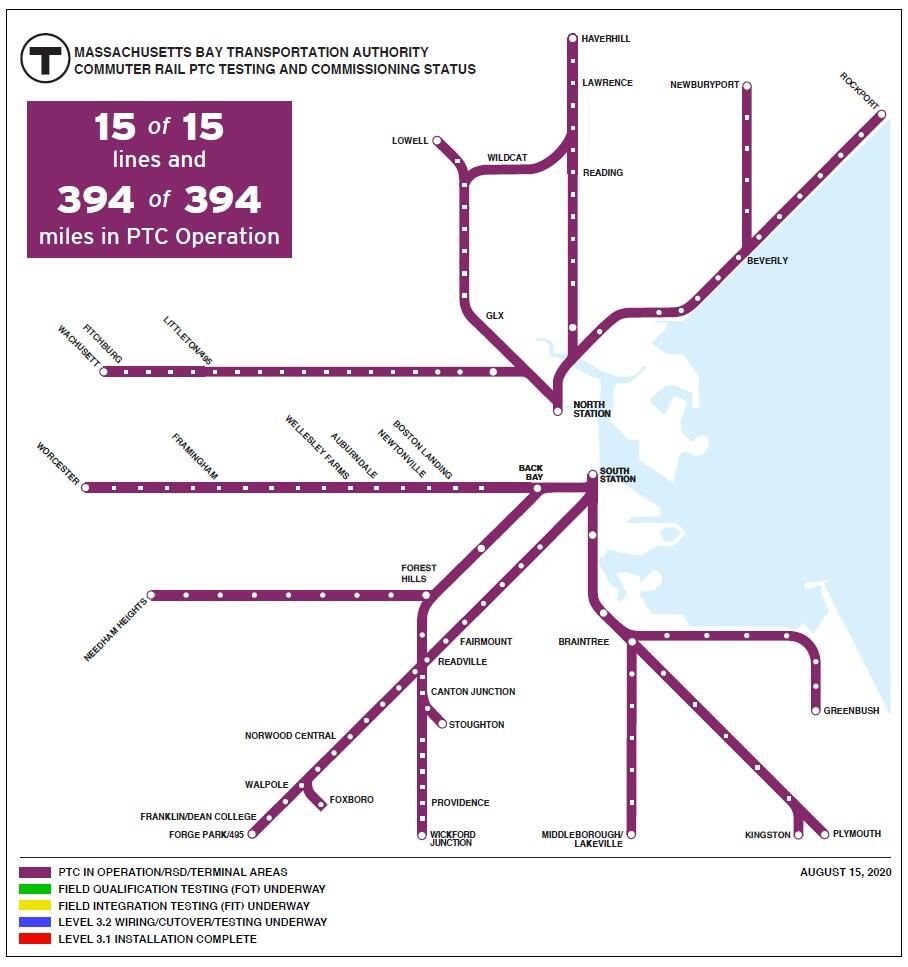
The MBTA is in full compliance FRA PTC regulations, completing the PTC System prior to the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) deadline of December 31, 2020.
- PTC is in operation on all of the MBTA’s Commuter Rail lines (394 of 394 route miles)—we placed the last segment in service on August 15, 2020.
- PTC equipment is installed and fully operational on all MBTA Commuter Rail revenue vehicles.
- We completed interoperability testing with tenant railroads (Amtrak, CSX, and Pan Am).
Phase I Timeline
PTC hardware and software components were installed around the commuter rail system and on each locomotive and control car. (A control car is a non-powered train coach that can control operation from the end of the train opposite the locomotive.)
After key milestones in the installation process were met in 2018, the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) granted the MBTA an extension until December 2020 for full deployment. To get an extension from the FRA, major work was required to be completed. It included:
- The installation of wayside equipment across the entire network
- Installation of computer equipment on board all locomotives and control cars
- Field qualification testing on the Stoughton Pilot Line
- PTC training of railroad personnel
Commuter Rail trains operate with PTC technology. PTC performance was monitored and adjusted accordingly, and quality testing ensured reliable safety monitoring will be delivered across the Commuter Rail system over long stretches of time and in all types of weather.
In addition, older signaling systems were upgraded to make them compatible with PTC. The upgrade has an added benefit: it makes them more reliable and much less likely to cause service delays.
As of December 2020, the MBTA Commuter Rail system, Amtrak, and freight railroads across the state are protected by PTC.
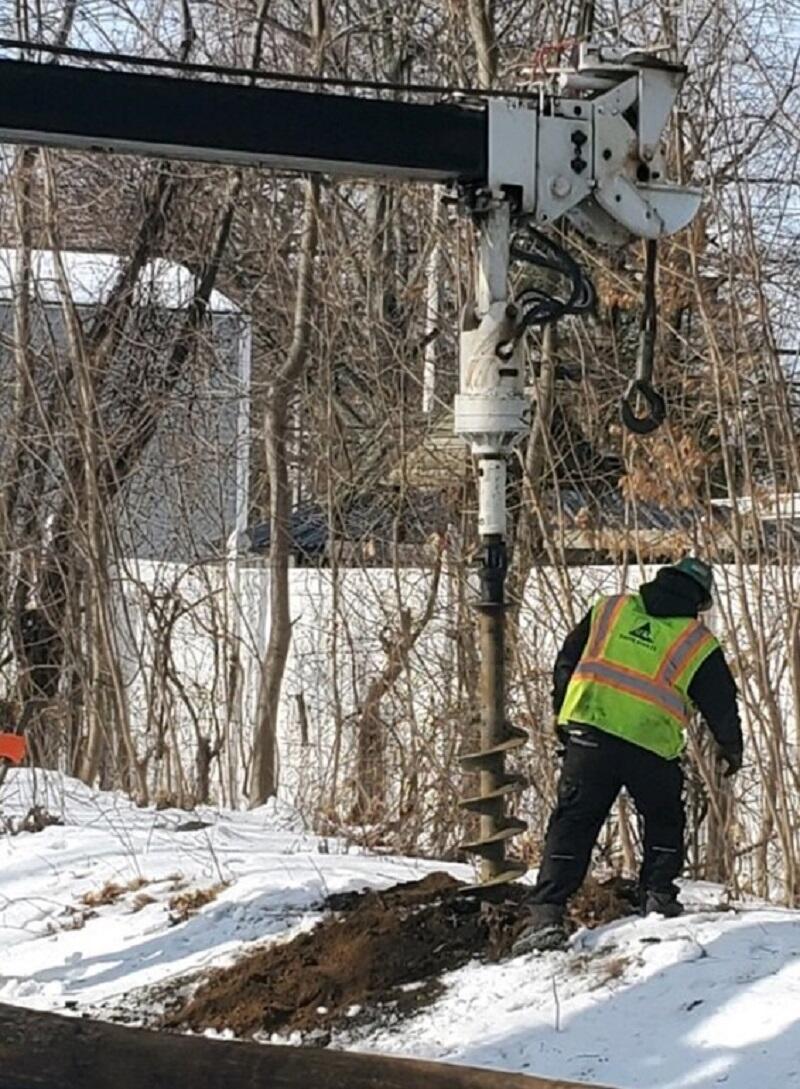
Phase I Photo Gallery
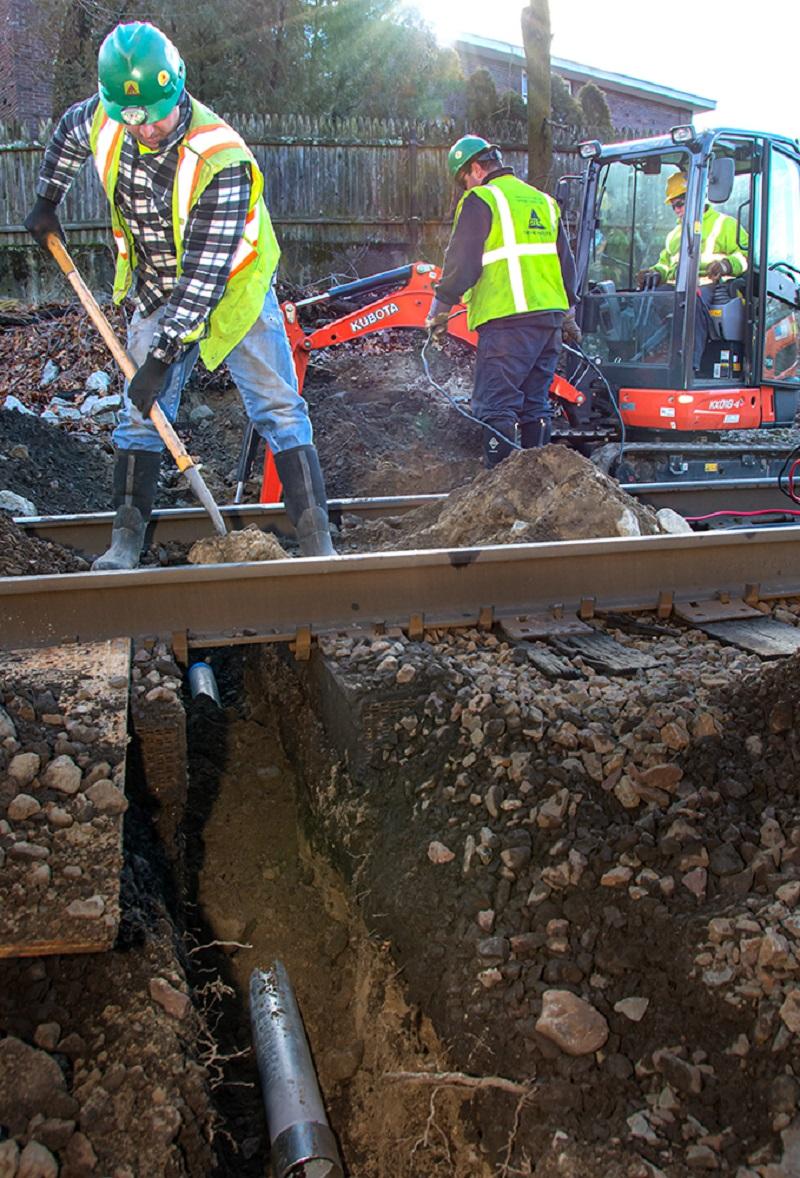

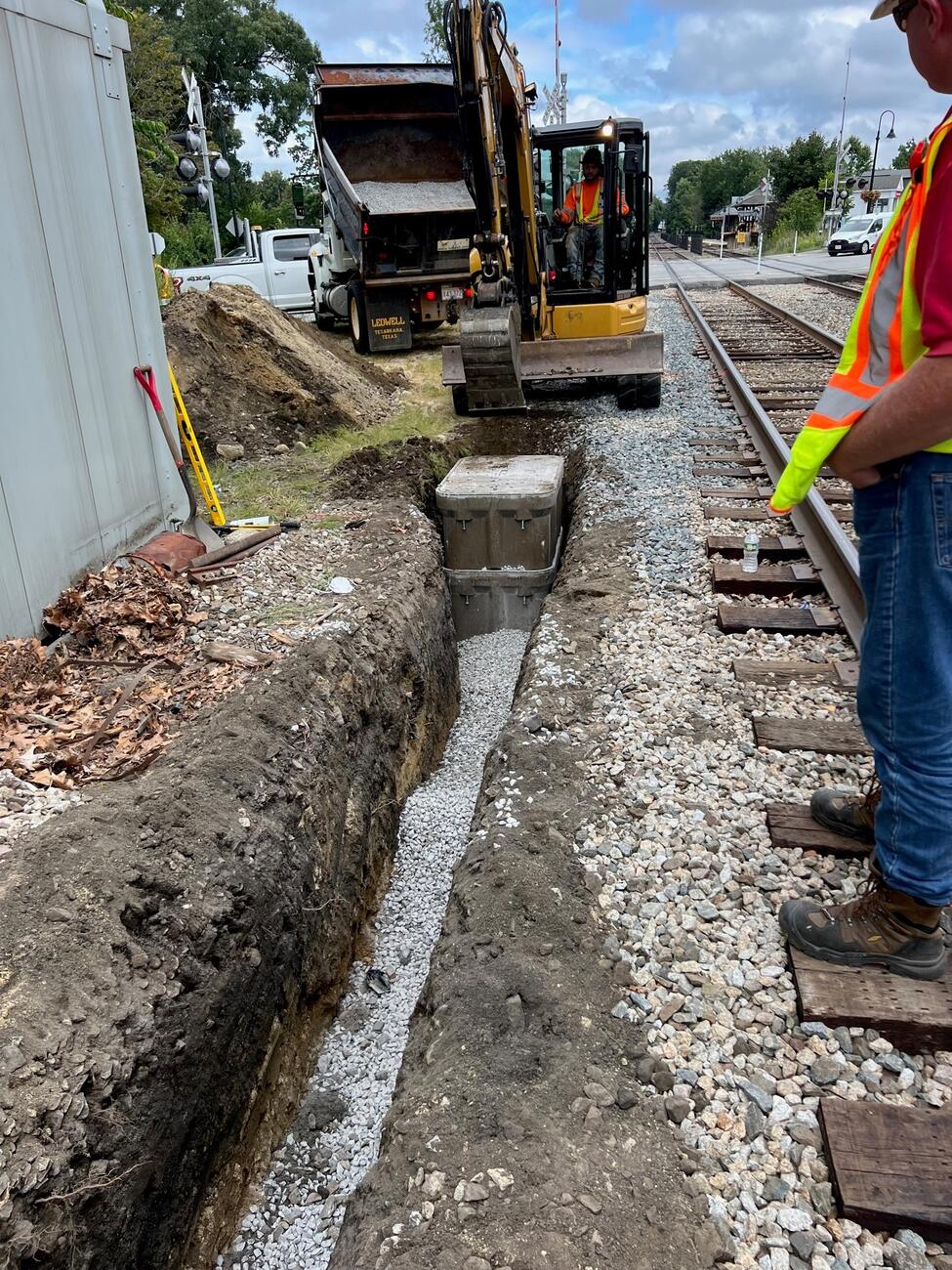
A crew excavates underneath the track where signal communication line will be installed as part of the PTC upgrades on the Franklin Line of the Commuter Rail (January 2020)
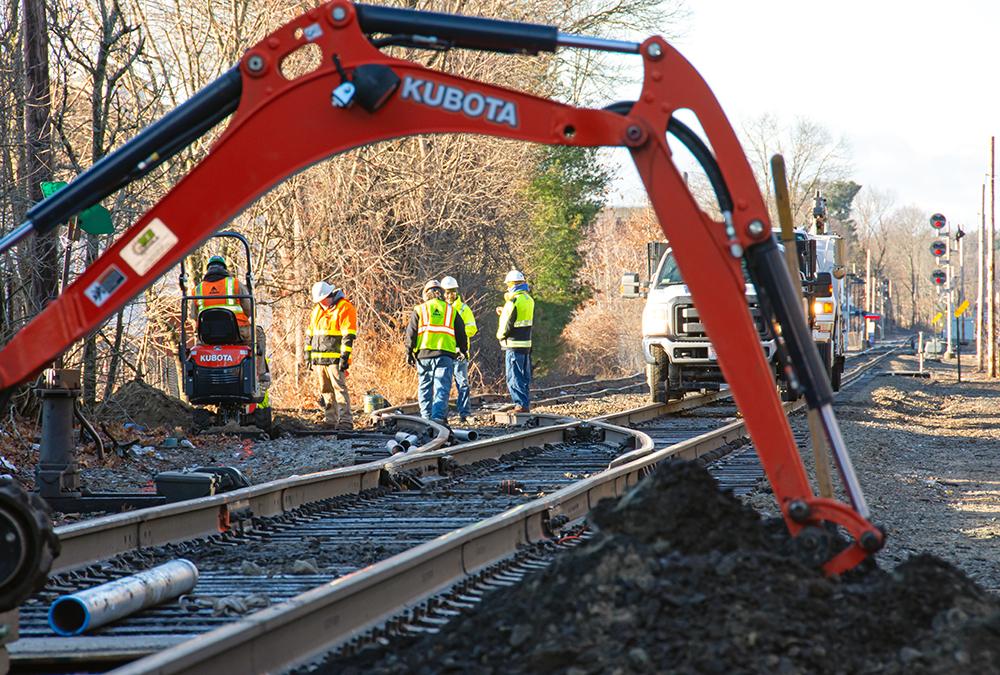
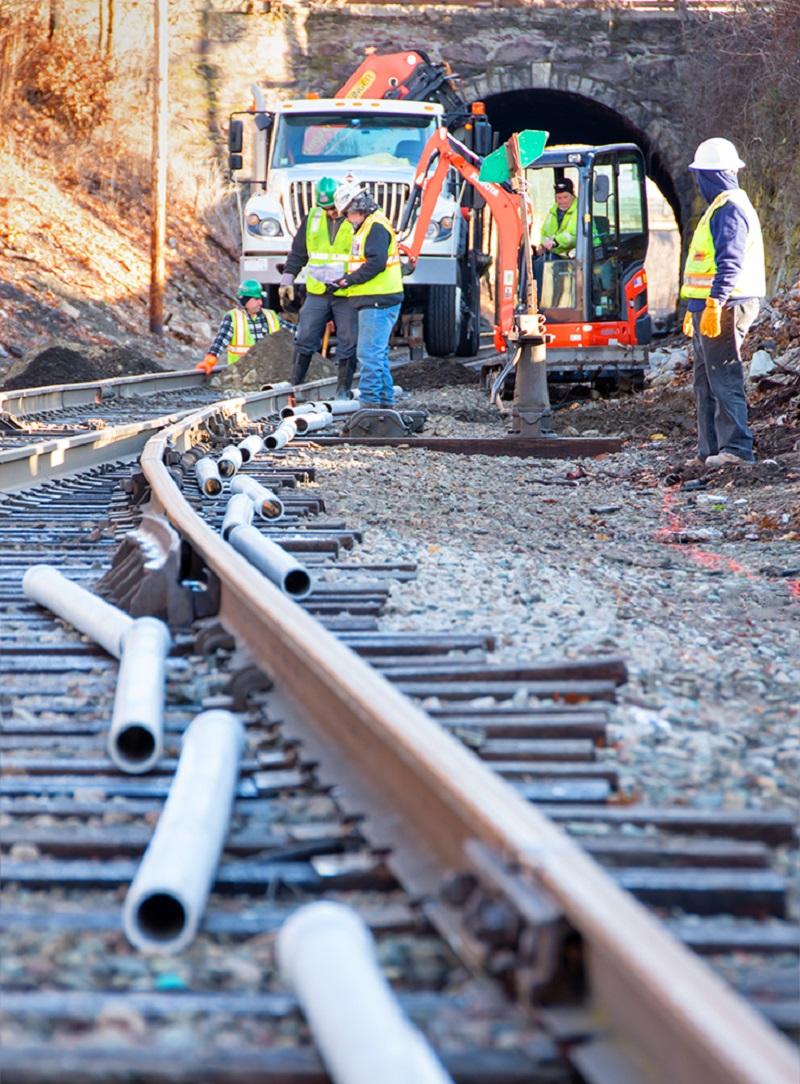


A crew prepares to install track signal communication line near Walpole Station on the Franklin Line of the Commuter Rail (January 2020)
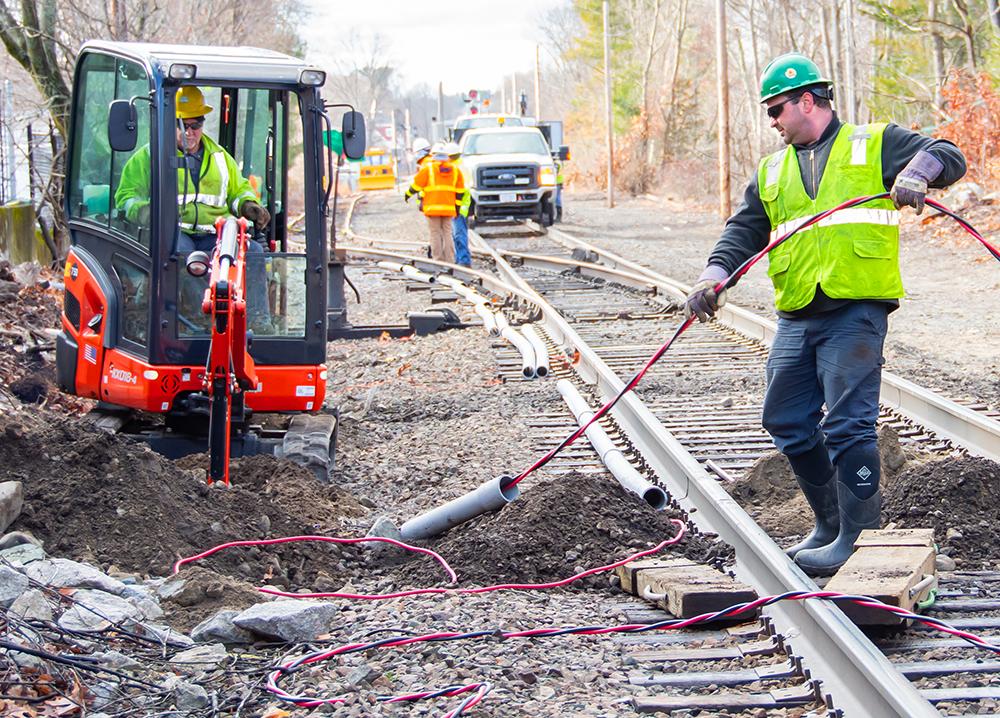

A crew installs track signal communication line near Walpole Station on the Franklin Line of the Commuter Rail (January 2020)
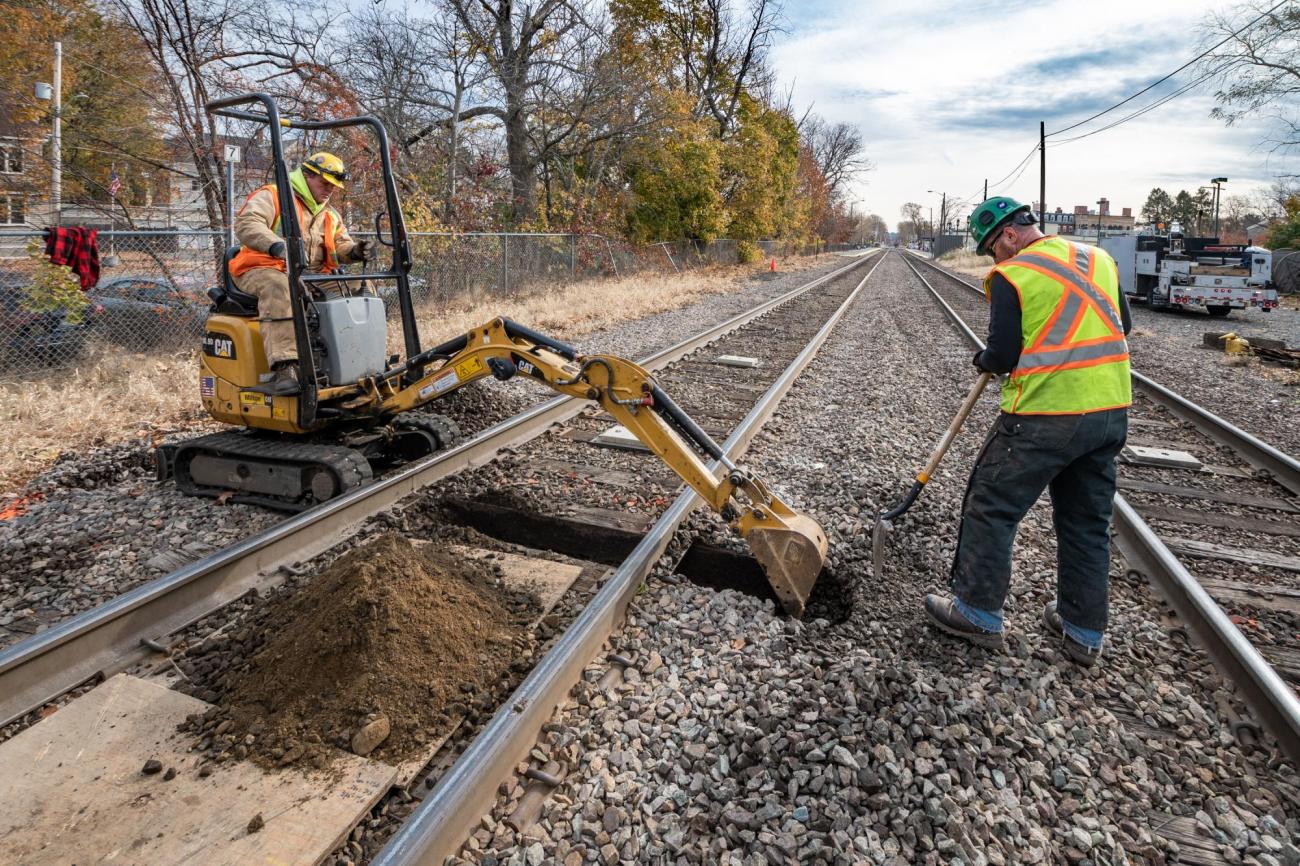

Crew members excavate under the track to prepare for power line installation as part of the PTC upgrades on the Lowell Line of the Commuter Rail (November 2019)
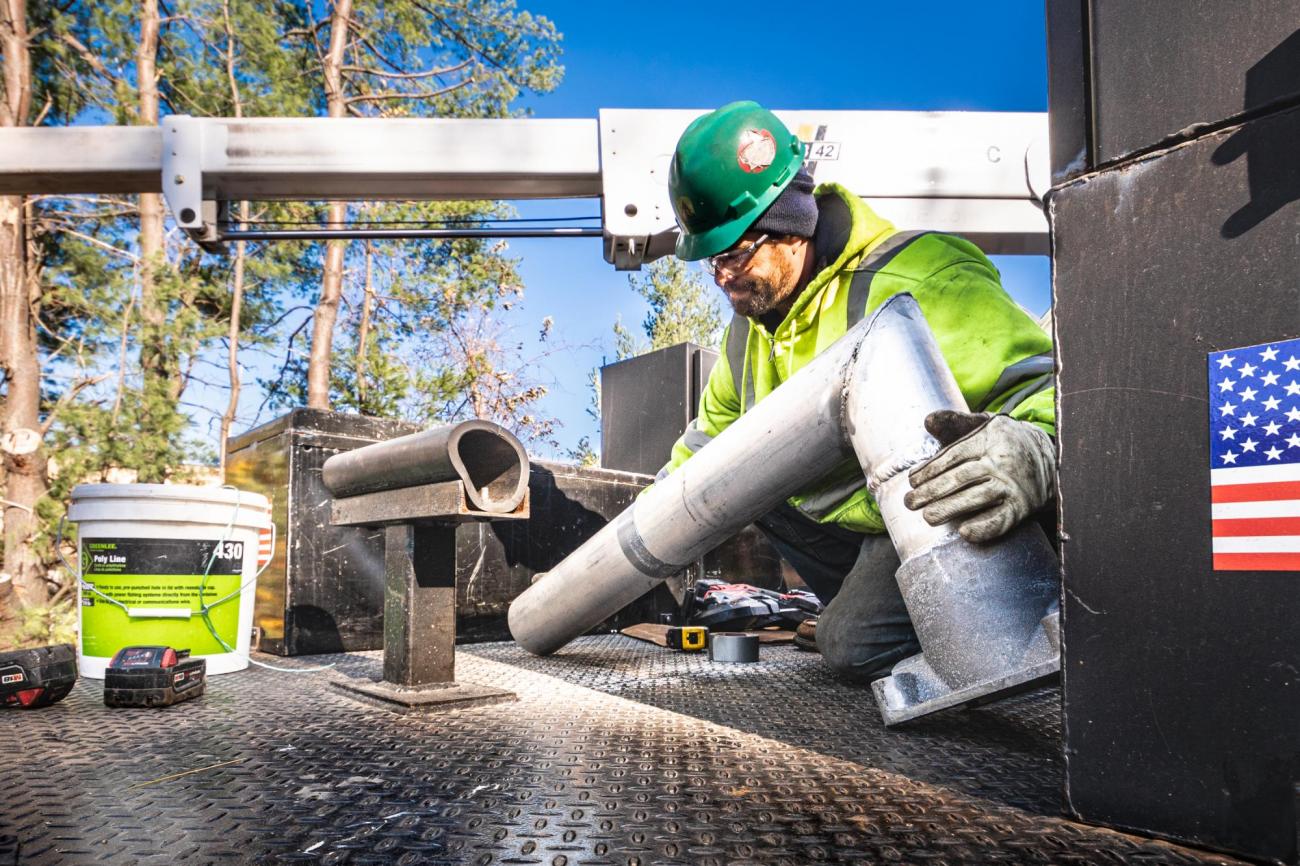

A crew member prepares PTC signal upgrades for installation on the Fitchburg Line of the Commuter Rail (November 2019)
Past Events
Contact Information
For all queries and comments related to Commuter Rail Positive Train Control, please contact the PTC Hotline at PTCProgram@mbta.com or 617-721-7506.
Recent Updates
Building a Better T
As part of our $9.6 billion, 5-year capital investment plan, we're renovating stations, modernizing fare collection systems, upgrading services for our buses, subways, and ferries, and improving the accessibility of the entire system.